Paradox Mindset Inventory - More Information
Do you want to learn more about the development of the Paradox Mindset Inventory?
Miron-Spektor, E., A. S. Ingram, J. Keller, W. K. Smith and M. W. Lewis (2018). "Microfoundations of organizational paradox: The problem is how we think about the problem." Academy of Management Journal 61(1): 26-45.
Do you want to learn more about paradoxes and a paradox mindset?
Books
Both/And Thinking: Embracing Creative Tensions to Solve Your Toughest Problems; Wendy Smith and Marianne Lewis (Harvard Business School Press, 2022).

We distilled 20 years of research on paradoxes and paradox mindsets in this book. This book help individuals and leaders develop the skills and practices to understand and navigate paradoxes in order to solve their toughest problems.
Articles
“Both/And” Leadership, Wendy Smith, Marianne Lewis and Michael Tushman Harvard Business Review, 2016
“Overwhelmed: Adopt a Paradox Mindset”; Ella Miron-Spektor and Wendy Smith INSEAD Working Knowledge, 2020
“Why the Paradox Mindset is the Key to Success” BBC, November 11, 2020
“Embrace the Paradox to Become a Better Leader” Wendy Smith, Marianne Lewis, Josh Keller, Ella Miron-Spektor December 21, 2021
Videos
How do you approach tensions at work? - Video on Paradox Mindsets
The Power of Paradox - Tedx Talk
Paradoxical Leadership - Video from Harvard Learning Innovation Labs
Wendy Smith: Adopt a Paradox Mindset - 2 minute video
Infographic
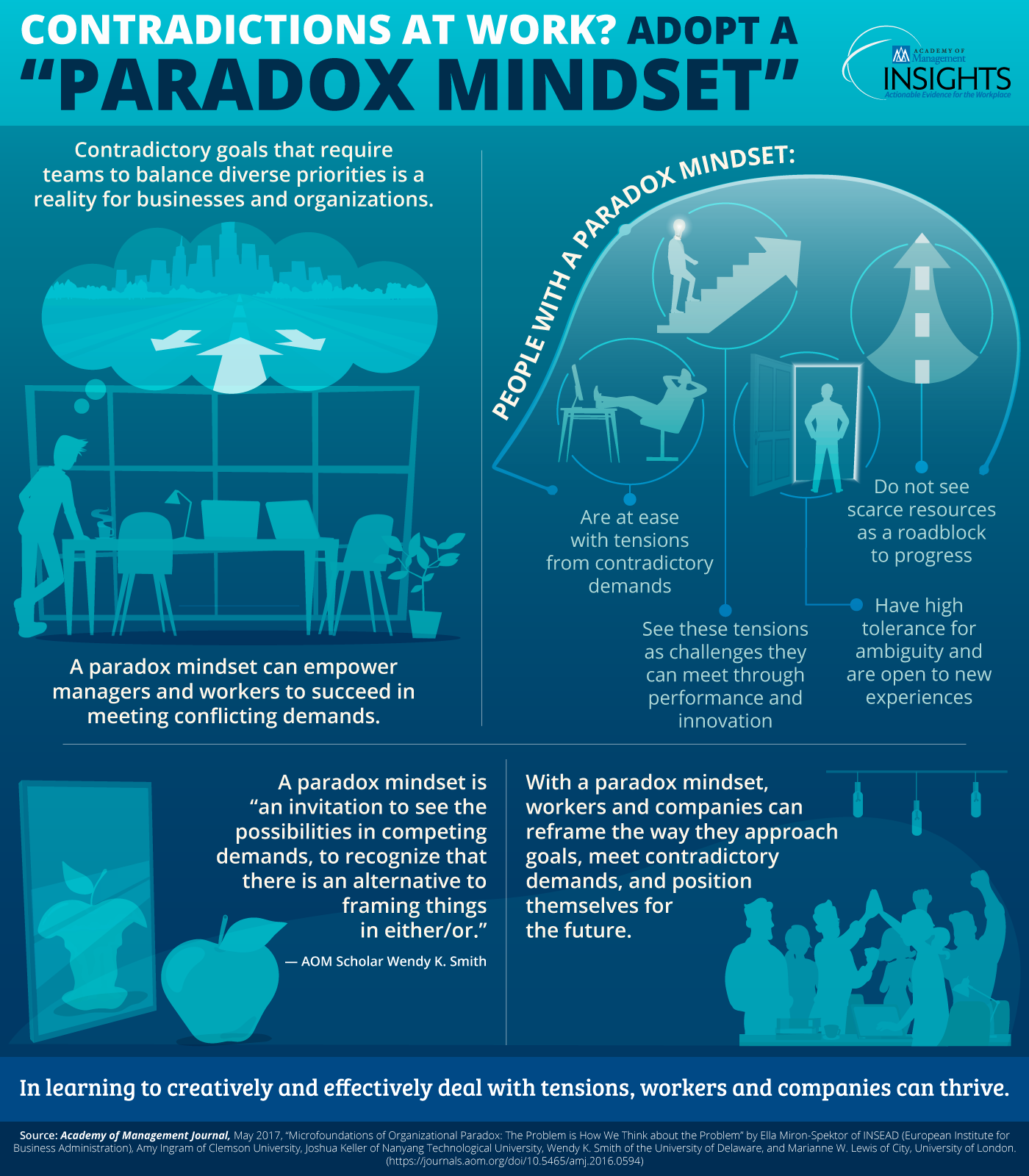
Contradictions at Work: Paradox Mindset Infographic
Academic Research
Keller, J., J. Loewenstein and J. Yan (2017). "Culture, Conditions and Paradoxical Frames." Organization Studies 38(3-4): 539-560.
Lewis, M. W. (2000). "Exploring paradox: Toward a more comprehensive guide." Academy of Management Review 25(4): 760-776.
Miron-Spektor, E., F. Gino and L. Argote (2011). "Paradoxical frames and creative sparks: Enhancing individual creativity through conflict and integration." Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 116(2): 229-240.
Smith, W. K. and M. W. Lewis (2011). "Toward a theory of paradox: A dynamic equilibrium model of organizing." Academy of Management Review 36(2): 381-403.
Smith, W. (2014). "Dynamic Decision Making: A Model of Senior Leaders Managing Strategic Paradoxes." Academy of Management Journal 57(6): 1592-1623.
Leung, A., Liou, S. Miron-Spektor, E., Koh, B., Chan, D., Eisenberg*, R., & Schneider, I. (2018). Middle ground approach to paradox: Within- and between-culture examination of the creative benefits of paradoxical frames. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 114 (3), 443-464.
Keller, J., J. Loewenstein and J. Yan (2017). "Culture, Conditions and Paradoxical Frames." Organization Studies 38(3-4): 539-560.
Miron-Spektor, E., Erez, M., & Naveh, E. (2011). The effect of conformists and attentive-to-detail members on team innovation: Reconciling the innovation paradox. Academy of Management Journal, 54 (4), 740–760.
Waldman, D., Putnam, L.L. Miron-Spektor, E., & Siegel, S.D. (2019). The role of paradox theory in decision making and management research. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 155, 1.